Absolutely! Here’s a 3000-word article on aluminum investment casting, formatted with your requested changes (replacing “ with `
` or `
` for headings):
Aluminum investment casting, also known as lost-wax casting, is a highly precise manufacturing process used to create intricate metal parts. This technique is particularly well-suited for aluminum alloys, offering a combination of lightweight properties, excellent corrosion resistance, and good mechanical strength. In this article, we delve into the intricacies of aluminum investment casting, exploring its process, advantages, applications, and future trends.

Investment casting is a manufacturing technique that involves creating a wax pattern of the desired part, coating it with a ceramic material to form a shell, melting out the wax, and then pouring molten metal into the resulting cavity. Aluminum, with its desirable properties, has become a popular choice for investment casting applications.
The investment casting process for aluminum involves several key steps:
Pattern Creation
The process begins with the creation of a precise wax pattern, replicating the final part. These patterns are typically made by injecting wax into a metal die.
Shell Building
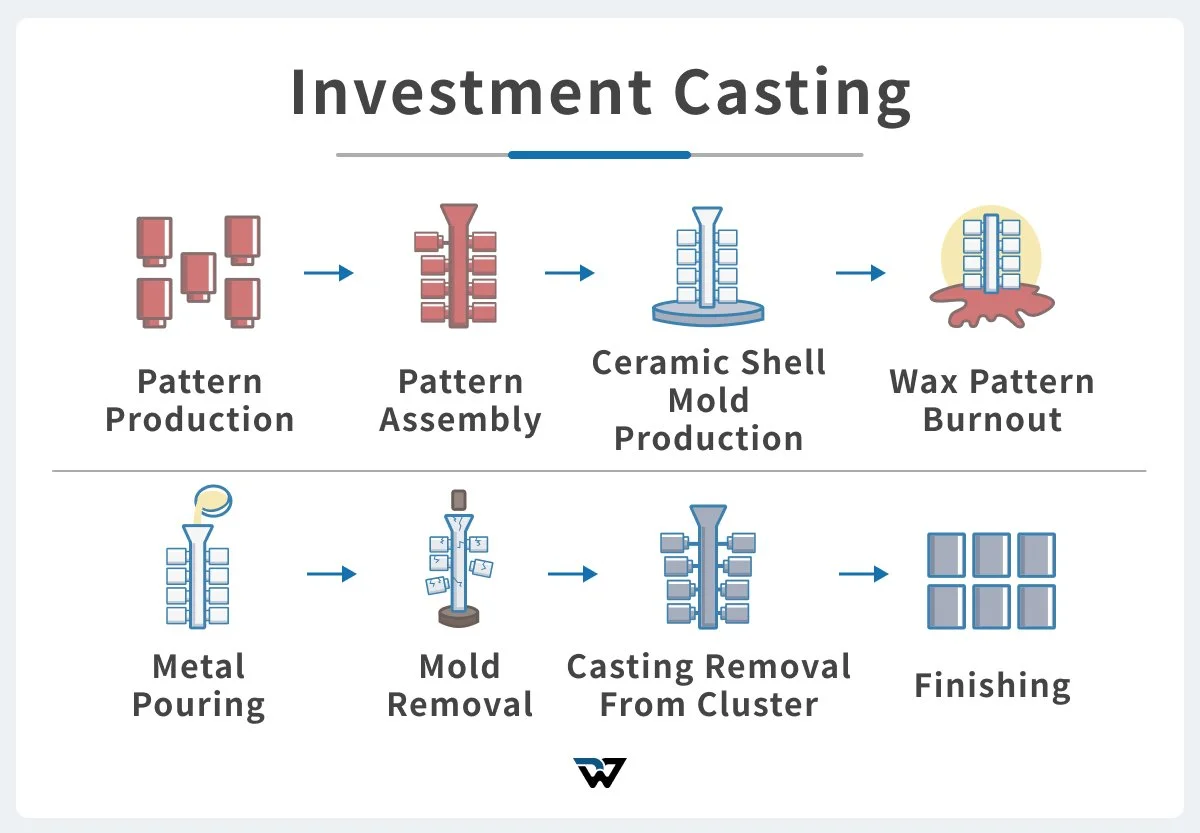
The wax pattern is then repeatedly dipped into a ceramic slurry and coated with refractory material (e.g., silica, alumina).
Wax Removal (Dewaxing)
The ceramic shell, containing the wax pattern, is heated in an autoclave or furnace.
Preheating the Shell
The ceramic shell is further heated to a high temperature, typically around 1000°C (1832°F).
Metal Pouring
Molten aluminum alloy is poured into the preheated ceramic shell.
Solidification and Cooling
The molten aluminum is allowed to solidify and cool within the ceramic shell.
Shell Removal (Knockout)
Once the aluminum casting has solidified, the ceramic shell is broken away using vibration, hammering, or chemical leaching.
Finishing and Inspection
The casting undergoes finishing processes such as grinding, machining, and surface treatments to achieve the desired dimensions and surface finish.
Aluminum investment casting offers numerous advantages over other casting methods:
High Dimensional Accuracy
The process allows for the creation of intricate and complex shapes with tight tolerances.
Excellent Surface Finish
Design Flexibility
Investment casting can accommodate complex geometries, including internal passages and undercuts.
Wide Range of Aluminum Alloys
Various aluminum alloys can be used in investment casting, allowing for customization based on specific application requirements.
Reduced Material Waste
The process minimizes material waste compared to machining from solid blocks.
Cost-Effectiveness for Complex Parts
Thin Wall Capabilities
Several aluminum alloys are commonly used in investment casting, each offering unique properties:
A356 Aluminum Alloy
This alloy is widely used for its excellent castability, corrosion resistance, and mechanical properties.
A357 Aluminum Alloy
Similar to A356, but with higher strength and ductility.
535 Aluminum Alloy (Almag 35)
Known for its high corrosion resistance and excellent polishing characteristics.
713 Aluminum Alloy
Designed for high-temperature applications.
Aluminum investment castings find applications in various industries:
Aerospace
Structural components, engine parts, and hydraulic system components.
Automotive
Engine components, suspension parts, and transmission components.
Medical
Surgical instruments, orthopedic implants, and medical devices.
Defense
Weapon components, military vehicle parts, and electronic housings.
Industrial Equipment
Pump components, valve bodies, and machinery parts.
Electronics
Heat sinks, electronic enclosures, and connectors.
Recreational Equipment
Bicycle components, marine hardware, and sporting goods.
Proper design is essential for successful aluminum investment casting:
Wall Thickness
Maintain uniform wall thickness to prevent shrinkage and distortion.
Draft Angles
Fillets and Radii
Tolerances
Gating and Risering
The field of aluminum investment casting continues to evolve with advancements in technology and materials:
Additive Manufacturing Integration
Combining additive manufacturing (3D printing) with investment casting to create complex wax patterns.
Advanced Alloys
Development of new aluminum alloys with enhanced properties, such as higher strength and improved corrosion resistance.
Automation and Robotics
Increased automation and robotics in investment casting processes to improve efficiency and reduce labor costs.
Digitalization and Simulation
Use of digital simulation tools to optimize casting designs and predict potential defects.
Sustainability
Focus on sustainable practices, such as recycling wax and metal, and reducing energy consumption.
Aluminum investment casting is a versatile and precise manufacturing process that offers numerous advantages for creating complex and high-quality metal parts. With its ability to produce intricate shapes, excellent surface finishes, and tight tolerances, aluminum investment casting is well-suited for a wide range of applications across various industries. As technology advances and new alloys are developed, the future of aluminum investment casting looks promising, with continued improvements in efficiency, quality, and sustainability.
